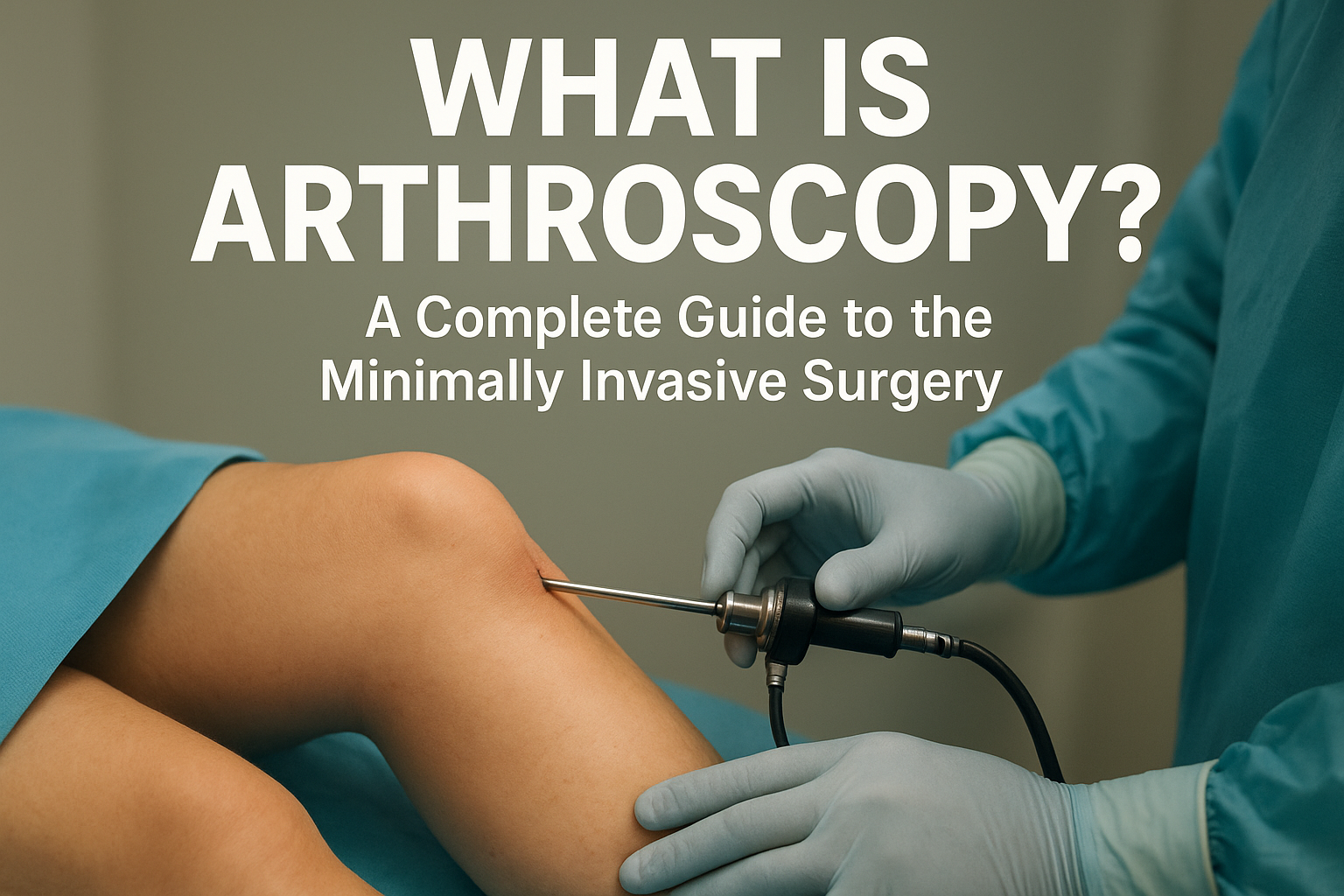
Arthroscopy is a modern surgical technique that allows doctors to diagnose and treat joint problems using a minimally invasive approach. Instead of making large incisions, surgeons use a small camera called an arthroscope, inserted through a tiny cut near the joint. This advanced method offers patients faster recovery, minimal pain, and reduced scarring compared to traditional open surgery.
How Does Arthroscopy Work?
During the procedure, the surgeon inserts the arthroscope—a thin tube with a camera and light—into the joint through a small incision. The high-definition camera transmits real-time images to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to view the inside of the joint clearly.
Specialized instruments are then used to repair, smooth, or remove damaged tissues. The small incision means minimal disruption to surrounding muscles and ligaments, leading to a quicker return to daily activities.
Common Joints Treated With Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy can be performed on several joints, including:
Knee Arthroscopy: For meniscus tears, ligament injuries, and cartilage damage.
Shoulder Arthroscopy: For rotator cuff repair, impingement, and instability.
Hip Arthroscopy: To treat labral tears or remove bone spurs.
Elbow Arthroscopy: For loose body removal and stiffness correction.
Ankle Arthroscopy: For cartilage damage and ligament reconstruction.
Wrist Arthroscopy: To treat ganglion cysts and ligament injuries.
Conditions Treated With Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopy helps diagnose and treat several joint disorders such as:
Torn ligaments or cartilage
Inflammation of the synovial membrane
Loose bone fragments within the joint
Damaged joint surfaces
Recurrent dislocations
Arthritis-related joint issues
Advantages of Arthroscopy
The benefits of this minimally invasive procedure are significant:
Smaller incisions and minimal scarring
Reduced postoperative pain
Shorter hospital stay or even same-day discharge
Faster healing and return to normal activities
Lower risk of infection and complications
Enhanced visualization for precise diagnosis
Preparation Before Arthroscopic Surgery
Before undergoing the surgery, patients typically go through several steps:
Medical Evaluation: Complete assessment to ensure fitness for anesthesia.
Imaging Tests: X-rays or MRI scans to understand joint damage.
Preoperative Instructions: Fasting guidelines and medication adjustments.
Discussion with Surgeon: Understanding potential risks and benefits.
Proper preparation ensures a smooth surgical experience and optimal recovery.
Recovery After Arthroscopy
Recovery duration depends on the joint involved and the extent of repair. Most patients can resume light activities within a few days.
Apply ice packs to reduce swelling.
Keep the incision clean and dry.
Follow prescribed physiotherapy exercises.
Avoid strenuous activity until the surgeon’s clearance.
With consistent rehabilitation, full recovery can occur in a few weeks to months.
Possible Risks and Complications
Though arthroscopy is generally safe, potential risks include:
Infection at the incision site
Bleeding or blood clots
Joint stiffness or swelling
Nerve or tissue damage (rare)
Choosing an experienced orthopedic surgeon minimizes these risks significantly.
Why Choose Arthroscopy Over Traditional Surgery
Arthroscopy stands out for its accuracy, minimal invasiveness, and faster recovery. It provides better visualization of the joint, allowing surgeons to diagnose and treat issues that may not appear clearly on imaging tests. For many patients, it means less downtime, less discomfort, and a quicker return to an active lifestyle.
Conclusion
Arthroscopy revolutionized joint care with smaller incisions, faster healing, and excellent results. It offers precision and comfort for patients seeking advanced orthopedic solutions.