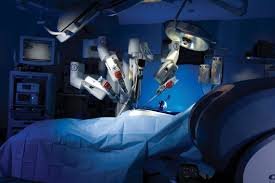
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, involves the use of robotic systems to aid surgeons in performing complex procedures with more precision, flexibility, and control than traditional techniques. These systems typically consist of a camera arm and mechanical arms with surgical instruments, all controlled by the surgeon from a console.
Importance of Robotic Surgery Precautions
While robotic surgery offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to implement specific precautions to mitigate risks associated with the technology and procedure. These precautions encompass preoperative planning, intraoperative measures, and postoperative care.
Preoperative Precautions
1. Comprehensive Patient Assessment
Medical History Review: Evaluate the patient’s medical history to identify any conditions that may complicate robotic surgery.
Imaging and Diagnostics: Utilize imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans to plan the surgical approach accurately.
2. Informed Consent
Educate the Patient: Ensure the patient understands the procedure, benefits, potential risks, and alternatives.
Discuss Potential Complications: Highlight possible complications specific to robotic surgery, such as equipment malfunction or conversion to open surgery.
3. Equipment Check and Maintenance
System Diagnostics: Perform thorough checks of the robotic system to ensure all components are functioning correctly.
Sterilization Protocols: Adhere to strict sterilization procedures to prevent infections.
Intraoperative Precautions
1. Surgical Team Coordination
Clear Communication: Maintain open lines of communication among all team members, especially since the surgeon operates from a console away from the patient.
Defined Roles: Assign specific roles and responsibilities to each team member to ensure efficiency and safety.
2. Patient Positioning
Proper Alignment: Ensure the patient is positioned correctly to prevent nerve damage or pressure injuries.
Secure Placement: Use appropriate padding and restraints to maintain patient stability throughout the procedure.
3. Equipment Monitoring
Real-time Surveillance: Continuously monitor the robotic system’s performance to detect any anomalies promptly.
Emergency Protocols: Be prepared to convert to traditional surgical methods if the robotic system fails.
Postoperative Precautions
1. Immediate Recovery Monitoring
Vital Signs Assessment: Closely monitor the patient’s vital signs to detect any immediate postoperative complications.
Pain Management: Provide adequate pain relief while monitoring for adverse reactions.
2. Infection Prevention
Wound Care: Educate the patient on proper wound care to prevent infections.
Follow-up Appointments: Schedule regular check-ups to monitor the healing process and address any concerns.
3. Patient Education
Activity Guidelines: Provide clear instructions on activity restrictions and gradual resumption of daily activities.
Symptom Awareness: Inform the patient about signs of potential complications that require immediate medical attention.