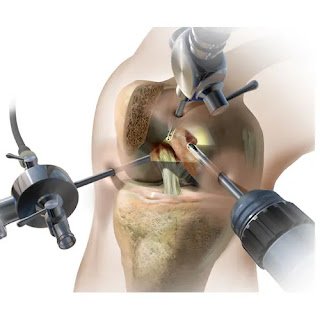
Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure used to examine, diagnose, and treat joint problems. A surgeon makes small incisions and inserts an arthroscope—a thin, flexible tube with a camera—into the joint. This provides a clear view of the joint’s interior on a monitor, allowing precise intervention.
What are the Common Joints Treated with Arthroscopy?
Knee Arthroscopy
- Repairing torn ligaments (e.g., ACL reconstruction)
- Treating meniscal tears
- Removing loose cartilage or bone fragments
Shoulder Arthroscopy
- Repairing rotator cuff tears
- Treating shoulder impingement
- Removing inflamed tissue or bone spurs
Hip Arthroscopy
- Treating labral tears
- Managing hip impingement
- Removing loose cartilage
Other Joints
- Wrist, ankle, and elbow arthroscopy are also common for addressing specific injuries or conditions.
Why Choose Arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery:
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions mean less scarring.
- Faster Recovery: Patients can often resume daily activities sooner.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Reduced blood loss and infection risk.
- Precise Diagnosis and Treatment: High-definition visuals allow for accurate intervention.
Conditions Treated with Arthroscopy
- Torn cartilage or ligaments
- Joint inflammation (e.g., synovitis)
- Damaged or loose cartilage
- Joint infections
- Osteoarthritis and related complications
The Arthroscopy Procedure: Step-by-Step
Preoperative Preparation
- A detailed medical history and imaging tests (e.g., MRI, X-ray) are conducted.
- Patients may need to fast before surgery.
The Procedure
- Small incisions are made near the joint.
- The arthroscope is inserted to visualize the joint.
- Surgical instruments are used to repair or remove damaged tissue.
Postoperative Care
- Patients are monitored for a few hours before being discharged.
- A rehabilitation plan, including physical therapy, is recommended for recovery.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from arthroscopy varies depending on the joint treated and the procedure performed. Here are general guidelines:
- Initial Days: Rest, ice, and elevate the affected joint to reduce swelling.
- Weeks 1–3: Begin light exercises as advised by a physical therapist.
- Weeks 4–6: Gradually increase activity levels, focusing on regaining strength and mobility.