Osteoporosis is one of the most common bone-related conditions, especially in older adults. It weakens the bones, making them fragile and more likely to break even with minor falls or injuries. Many people are unaware that they have osteoporosis until they suffer a fracture. Understanding how osteoporosis affects bone health and learning preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
What is Osteoporosis?
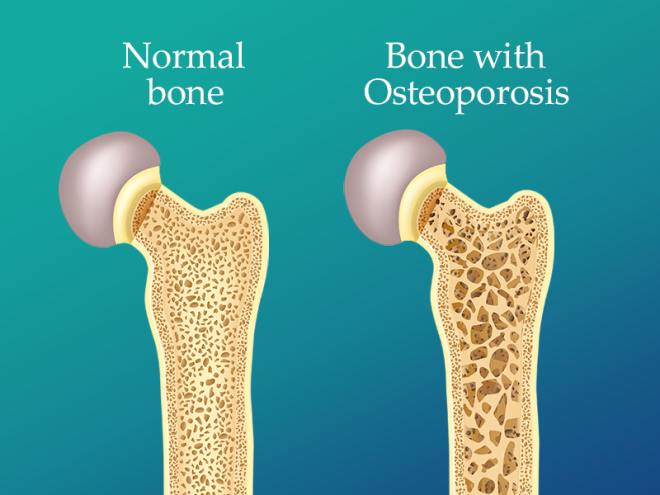
Osteoporosis is a condition where bone density decreases over time. Healthy bones are dense and strong, but when osteoporosis sets in, they become porous and brittle. This loss of bone strength often occurs silently and gradually, leading to an increased risk of fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, and wrist.
How Osteoporosis Affects Bone Health
Loss of Bone Density – The bones lose calcium and other minerals, making them weak.
Fragile Bones – Even small stresses, such as bending or coughing, can cause fractures.
Spinal Deformities – Osteoporosis may lead to compression fractures in the spine, causing back pain, loss of height, and a stooped posture.
Slower Healing – Fractures in osteoporotic patients take longer to heal, affecting mobility and independence.
Increased Risk of Complications – Hip fractures, for example, can lead to long-term disability in elderly patients.
What are the Risk Factors for Osteoporosis?
Age: Risk increases with age, especially after 50.
Gender: Women are more prone, particularly after menopause due to reduced estrogen levels.
Family History: A history of osteoporosis increases the likelihood.
Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol, and lack of exercise can weaken bones.
Poor Nutrition: Low calcium and vitamin D intake significantly contribute to bone loss.
What are the Symptoms of Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is often called a “silent disease” because it shows no symptoms until a fracture occurs. Some early signs may include:
Gradual loss of height
Stooped or hunched posture
Sudden fractures from minor injuries
Persistent back pain
Ways to Prevent Osteoporosis
While osteoporosis cannot always be completely prevented, there are many ways to maintain stronger bones and reduce risks.
1. Eat a Bone-Healthy Diet
Calcium-rich foods such as milk, cheese, yogurt, almonds, and leafy greens strengthen bones.
Vitamin D from sunlight, fish, and fortified foods helps the body absorb calcium.
2. Stay Physically Active
Weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, and dancing improve bone strength.
Strength training builds muscle, which supports and protects bones.
3. Avoid Harmful Habits
Quit smoking and reduce alcohol intake, as both damage bone health.
4. Regular Health Check-ups
Bone density tests (DEXA scans) help detect early signs of osteoporosis.
Consulting an orthopedic specialist ensures timely treatment and guidance.
5. Medications and Supplements
In some cases, doctors may prescribe calcium and vitamin D supplements.
Medications may be recommended to slow down bone loss and improve density.
Living with Osteoporosis
With the right care, lifestyle modifications, and medical support, people with osteoporosis can still lead active and healthy lives. Preventing falls, maintaining good posture, and following a nutritious diet are key to long-term bone health.